
Accurate blood pressure measurement
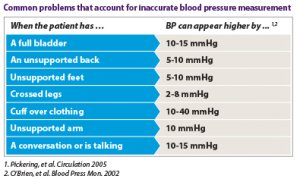 As a standard part of many physicians’ office workflows, measuring blood pressure may seem like a normal routine. But seemingly minor issues can impact blood pressure measurement, artificially inflating a patient’s blood pressure by anywhere from two to 40 mmHg.
As a standard part of many physicians’ office workflows, measuring blood pressure may seem like a normal routine. But seemingly minor issues can impact blood pressure measurement, artificially inflating a patient’s blood pressure by anywhere from two to 40 mmHg.
May is High Blood Pressure Education Month, an opportune time to reevaluate blood pressure measurement processes and talk to patients about managing their high blood pressure. Here are several ways you can make sure a patient’s blood pressure is accurately measured:
1. The patient’s feet are flat on the floor, and legs are uncrossed.
2. The patient’s arm and back are properly supported.
3. The patient doesn’t need to use the restroom and can comfortably remain still.
4. The patient’s arm is bare, and the sphygmomanometer cuff is on skin, not over any clothing.
5. The patient is not speaking and has had at least three minutes of quiet time prior to the measurement.
If a patient talks during the measurement, for example, or if the patient’s feet aren’t flat on the floor, there’s a chance that blood pressure measurement will give a falsely high reading. This could lead to a prescription for an unnecessary, potentially harmful, medication. At the same time, other factors can contribute to unidentified and untreated hypertension, which can be deadly.
Incorporating these standardized principles into practice workflows is a key element of the AMA’s Improving Health Outcomes initiative. A pilot program involving multiple clinical sites in two states is implementing principles of safe design into the ambulatory setting to improve outcomes around hypertension. Similar approaches, such as hospitals using checklists to reduce central-line infections, have seen successful results.Taking the checklist approach to blood pressure management can help ensure quality care in screening for and treating patients with high blood pressure, preventing the development of heart disease and stroke down the road.
To apply safe design principles to blood pressure management, the AMA is collaborating with researchers at Johns Hopkins University and the pilot sites to develop and test a set of evidence-based recommendations, based on a simple framework called the M.A.P. for achieving optimal hypertension control:
• easuring blood pressure accurately every time it’s measured
• cting rapidly to address high blood pressure readings
• artnering with patients to promote self-management of high blood pressure
The pilot sites are integrating best evidence into each step of the M.A.P. framework. For example, the AMA is incorporating successful elements of a program at Johns Hopkins’ Center to Eliminate Cardiovascular Health Disparities in designing resources to help practices engage patients in better self-management.RELATED VIDEO


Share this Post
Related posts
Most accurate Blood pressure Monitors
Your blood pressure is creeping up a bit, so you’re finally taking your doctor’s advice and shopping for a home blood-pressure…
Read MoreMost accurate Blood pressure Monitors Consumer Reports
Trackers provide insight about habits and health, but using one might also help you shed a few pounds. Neil Busis, M.D…
Read More











